
The Excretory System
The Parts of the System
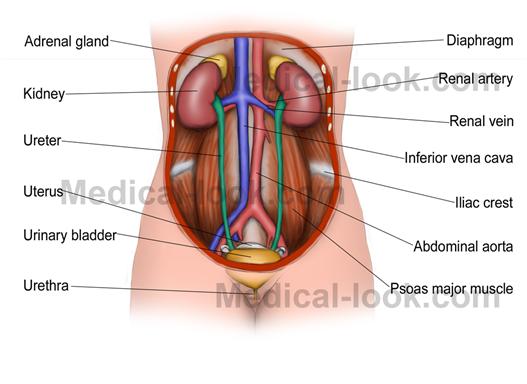
The Excretory System is made up of many different organs which are located all throughout the body. However, the majority of the organs are located in the lower abdomen, which is shown in the diagram at the right. This diagram contains the major organs of the Excretory System, such as the Kidney, Ureter, Urinary Bladder, and Urethra. Other members of this system include the liver, the lungs, and the skin. Below is a list of all the organs in this system, along with a description of their function in the Excretory System.
The processes of the Excretory System begin in the liver. The liver is a large organ in the body that regulates glycogen storage and breaks down unneeded wastes in the body. Liver cells are able to turn complex molecules into simple molecules, as well as turn toxic substances intro harmless ones. This is seen in the case of ammonia, which is turned into the harmless fluid urea when it passes through the liver. The liver is vital to the Excretory System because it turns wastes such as ammonia into harmless fluids that are passed on to the kidneys.
Source: http://www.desktopclass.com/education/9th-10th/excretion-10th-biology-chapter-13-lesson-1.html
Source: http://library.thinkquest.org/07aug/01618/excretory.html
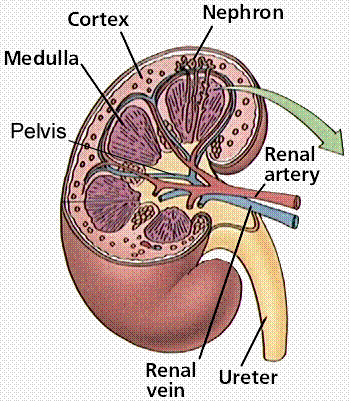
The Excretory System continues in the kidneys, which are the most important organ in the system. Urea and other harmless wastes come from liver and the circulatory system to the kidneys to be turned into different compounds. Blood containing wastes flows into the kidneys and past the nephrons, which are structures in the kidney that filter out wastes through diffusion. The blood then flows out of the kidneys, free of wastes except for carbon dioxide. Wastes from the liver are also deposited in the kidneys. The kidneys are vital to the Excretory System because they filter out most wastes from the system and turn them into urine so they can later be excreted.
Source: http://www.gonzaga.k12.nf.ca/academics/science/sci_page/biology/homeostasis_notes.htm
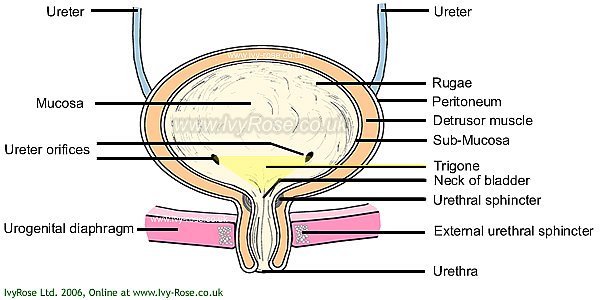
While the ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra are and should be counted as three separare organs, they are grouped together here because of their similarity in function: carrying the urine produced by the kidneys to the outside of the body. The ureters are muscular tubes extending from each kidney to the urinary bladder. Their function is to propel urine from the kidneys into the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular, elastic organ whose function is to contain urine until it is time for it to be excreted. The urethra is connected to the urinary bladder. It is simply a tube that is connected to the urinary bladder that runs to the outside of the body. It's function is to completely remove urine from the body. These three organs are vital to the excretory System because they completely remove metabolic wastes from the body.
Source:http://www.ivy-rose.co.uk/HumanBody/Urinary/Urinary_Bladder_Urethra_Female.php